The Thirteen Colonies Map Answer Key provides a detailed overview of the thirteen British colonies that existed in North America from the 17th to the 18th centuries. This guide offers a comprehensive examination of their geographical locations, economic activities, social structures, and political systems, shedding light on the formative years of the United States.
Through an in-depth analysis of maps, historical documents, and expert insights, this guide unravels the complex tapestry of colonial America, exploring the factors that shaped its development and ultimately led to the American Revolution.
Historical Context
The thirteen colonies played a pivotal role in the foundation and development of the United States. Established by European settlers in the 17th and 18th centuries, these colonies stretched along the Atlantic coast of North America.
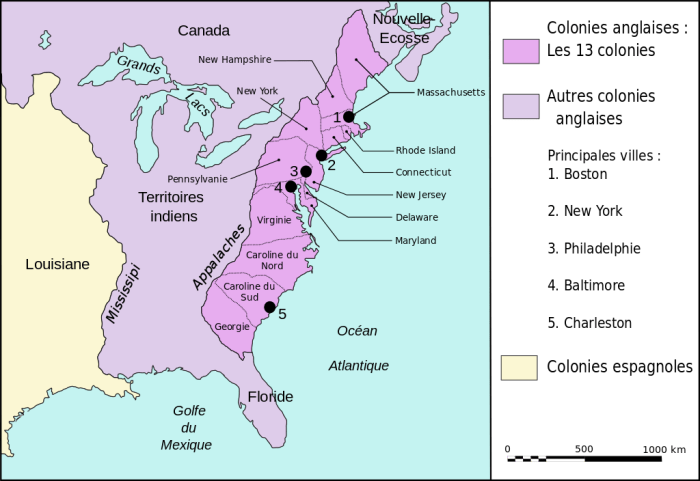
Geographically, the thirteen colonies were located between present-day Maine and Georgia. Their boundaries were defined by natural features such as rivers, mountains, and the Atlantic Ocean.
Map Analysis
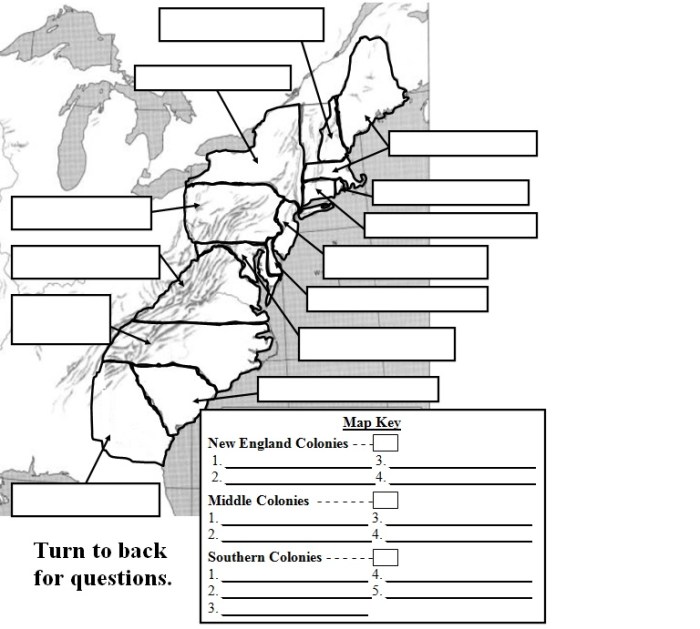
Major Cities, Rivers, and Landmarks
- Boston, Massachusetts: A major port city and center of commerce.
- New York City, New York: A hub for trade and immigration.
- Philadelphia, Pennsylvania: A cultural and political center.
- Mississippi River: A vital waterway for transportation and trade.
- Appalachian Mountains: A natural barrier that influenced settlement patterns.
- Plymouth Rock: The landing site of the Pilgrims in 1620.
Geographical Features and Development
The colonies’ geographical features had a significant impact on their development. The Atlantic coast provided access to trade and fishing, while the interior offered fertile land for agriculture. The Appalachian Mountains served as a barrier to westward expansion, but also provided resources such as timber and minerals.
Economic and Social Development
Economic Activities and Industries
- Agriculture: The primary economic activity, with crops such as tobacco, rice, and wheat.
- Trade: The colonies exported raw materials and imported manufactured goods.
- Fishing: A major industry along the Atlantic coast.
- Shipbuilding: A key industry in New England.
Social Structure and Demographics
The social structure of the colonies was hierarchical, with a small elite of wealthy landowners and merchants at the top and a majority of farmers and laborers at the bottom. The population was diverse, with immigrants from England, Ireland, Scotland, Germany, and Africa.
Factors Contributing to Growth
- Abundant natural resources
- Skilled workforce
- Growing demand for colonial goods
Political and Cultural Exchange
Political Systems and Governance
The colonies had varying forms of government, ranging from royal colonies directly controlled by the British crown to self-governing colonies with elected assemblies.
Cultural Influences and Exchanges
The colonies were influenced by a mix of European and Native American cultures. They developed their own distinct identities, but maintained strong ties to their European homelands.
Role in American Identity
The thirteen colonies played a central role in shaping American political and cultural identity. They were the birthplace of ideas such as self-government and individual liberty.
Road to Independence: Thirteen Colonies Map Answer Key
Events and Factors Leading to Revolution
- British economic policiesthat favored British merchants
- Growing sense of self-reliance and autonomy among colonists
- Enlightenment ideasthat emphasized natural rights and limited government
Role of the Colonies in Independence, Thirteen colonies map answer key
The thirteen colonies were at the forefront of the American Revolution. They organized the Continental Army and Congress, and declared independence from Great Britain in 1776.
Impact of the Revolution
The Revolution resulted in the establishment of the United States of America as an independent nation. It also had a profound impact on global politics and inspired revolutions around the world.
Popular Questions
What is the significance of the thirteen colonies in American history?
The thirteen colonies played a pivotal role in the founding of the United States. They were the birthplace of the American Revolution and the crucible in which the ideals of liberty, democracy, and self-governance were forged.
What were the major economic activities in the thirteen colonies?
The colonies had diverse economies, with agriculture being the dominant industry. Major crops included tobacco, rice, indigo, and wheat. Other important economic activities included fishing, shipbuilding, and trade.
What were the social and political structures of the thirteen colonies?
Colonial society was hierarchical, with a small elite at the top and a large majority of farmers, artisans, and laborers at the bottom. The colonies had representative assemblies, but ultimate authority rested with the British Crown.