Food chains food webs and energy pyramid worksheet – The Food Chains, Food Webs, and Energy Pyramid Worksheet is a comprehensive resource designed to provide students with an in-depth understanding of the intricate relationships between organisms within ecosystems. This worksheet explores the fundamental concepts of food chains, food webs, and energy pyramids, equipping students with a solid foundation in ecological principles.
Through engaging activities and data analysis, students will gain a deeper comprehension of the flow of energy through ecosystems, the roles of different trophic levels, and the importance of maintaining ecological balance.
Food Chains and Food Webs: Food Chains Food Webs And Energy Pyramid Worksheet
Food chains and food webs are fundamental concepts in ecology that describe the transfer of energy and nutrients through different organisms in an ecosystem.
Definition and Overview
A food chain is a linear sequence of organisms through which nutrients and energy pass, starting with a producer and ending with a top predator. Each organism in the chain consumes the one below it, and is in turn consumed by the one above it.
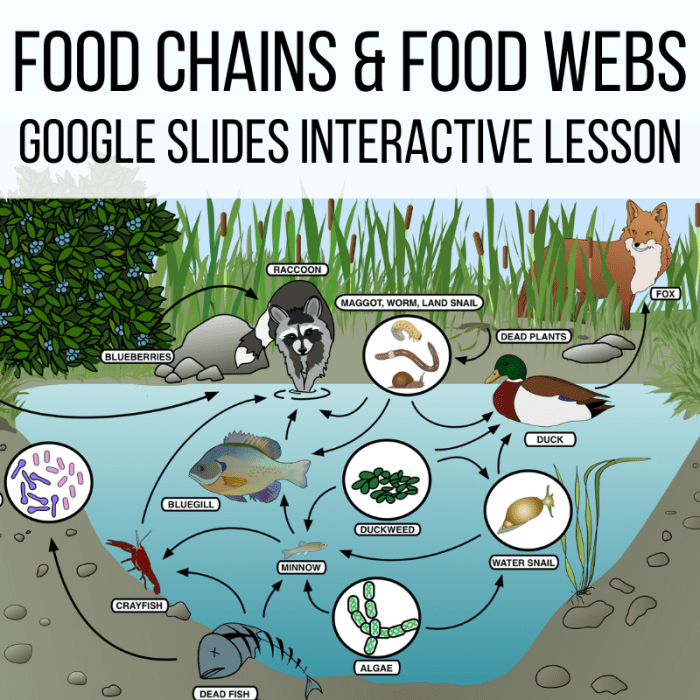
A food web is a more complex network of interconnected food chains, where multiple organisms can consume and be consumed by a variety of others.
Food chains and food webs provide insights into the structure and dynamics of ecosystems, and help us understand the flow of energy and nutrients through different trophic levels.
Components of Food Chains and Food Webs
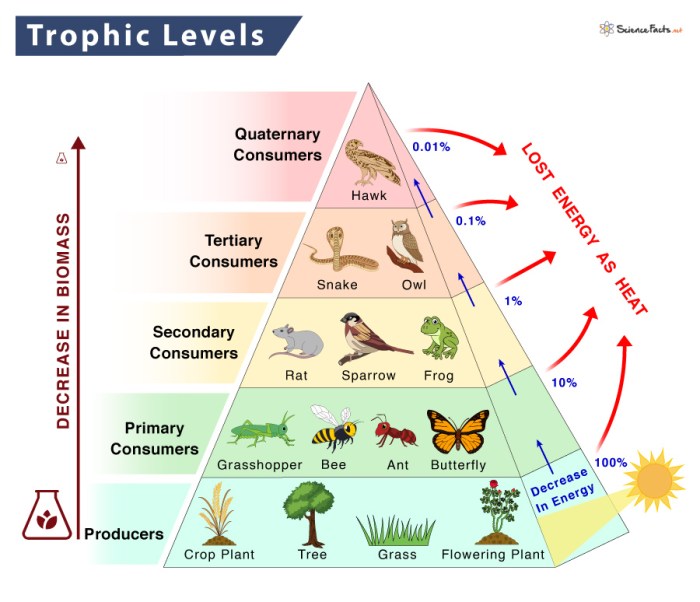
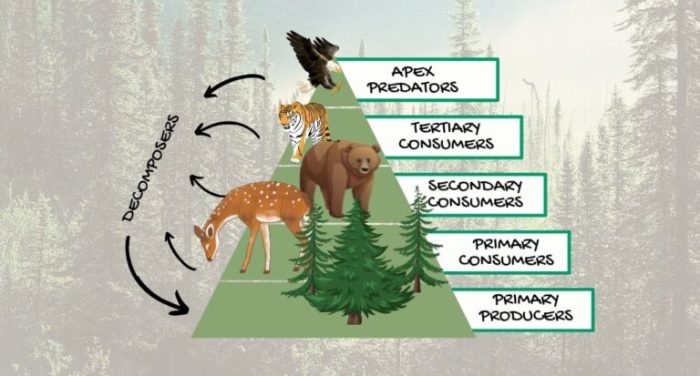
Food chains and food webs consist of different trophic levels, which represent the position of organisms in the energy flow:
- Producers:Organisms that can produce their own food through photosynthesis or chemosynthesis.
- Consumers:Organisms that cannot produce their own food and must consume other organisms.
- Decomposers:Organisms that break down dead organisms and recycle nutrients back into the ecosystem.
Consumers are further classified into:
- Primary consumers:Herbivores that consume producers.
- Secondary consumers:Carnivores that consume primary consumers.
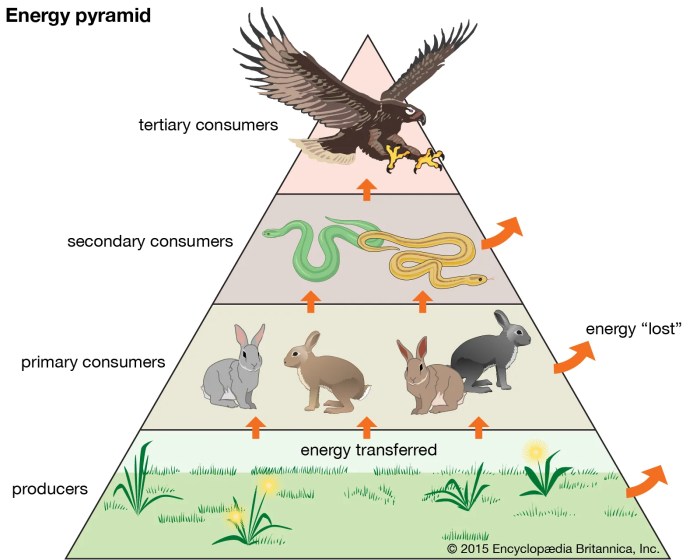
- Tertiary consumers:Carnivores that consume secondary consumers.
Energy Flow in Food Chains and Food Webs
Energy flows through food chains and food webs in a unidirectional manner, from producers to top predators. At each trophic level, a significant portion of energy is lost as heat or is used for metabolic processes.
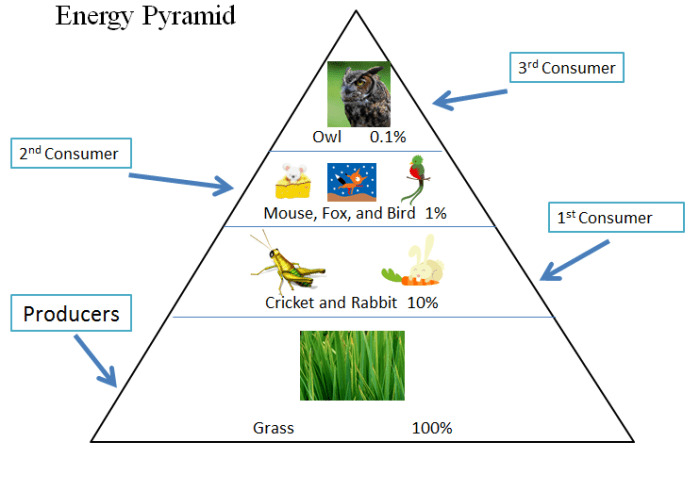
Energy pyramidsare graphical representations of the energy loss at each trophic level. They show that the amount of energy available to organisms decreases as we move up the food chain.
Photosynthesis is the primary mechanism through which energy enters food chains and food webs, converting light energy into chemical energy stored in plants.
Worksheet Activities, Food chains food webs and energy pyramid worksheet
Worksheet Activities:
- Identify trophic levels:Students will analyze a food chain or food web and identify the different trophic levels.
- Construct food chains and food webs:Students will create their own food chains and food webs based on given data.
- Calculate energy loss:Students will use an energy pyramid to calculate the energy loss at different trophic levels.
Data Table: Energy Flow in a Food Chain:
| Trophic Level | Organism | Energy (kcal/m2/year) |
|---|---|---|
| Producer | Grass | 10,000 |
| Primary consumer | Grasshopper | 1,000 |
| Secondary consumer | Spider | 100 |
| Tertiary consumer | Bird | 10 |
Essential FAQs
What is the difference between a food chain and a food web?
A food chain is a linear sequence of organisms through which energy and nutrients pass, while a food web is a more complex network of interconnected food chains, representing the feeding relationships within an ecosystem.
What is the role of producers in a food chain?
Producers are organisms, typically plants, that use sunlight to convert inorganic matter into organic compounds through photosynthesis, providing the foundation of energy and nutrients for all other organisms in the ecosystem.
How does energy flow through a food chain?
Energy flows unidirectionally through a food chain, from producers to consumers, with approximately 10% of the energy transferred to each subsequent trophic level.