Embark on an educational journey with our Phylogenetic Tree Practice Worksheet with Answers, a comprehensive resource designed to enhance your understanding of evolutionary relationships. This worksheet delves into the intricacies of phylogenetic trees, providing a solid foundation for exploring the diverse tapestry of life on Earth.
As you navigate through this worksheet, you will gain insights into the fundamental concepts of phylogenetic trees, the methodologies employed in their construction, and the wealth of information they can reveal about the evolutionary history of species. Prepare to engage in a thought-provoking exploration of the interconnectedness of all living organisms.
Phylogenetic Tree Basics
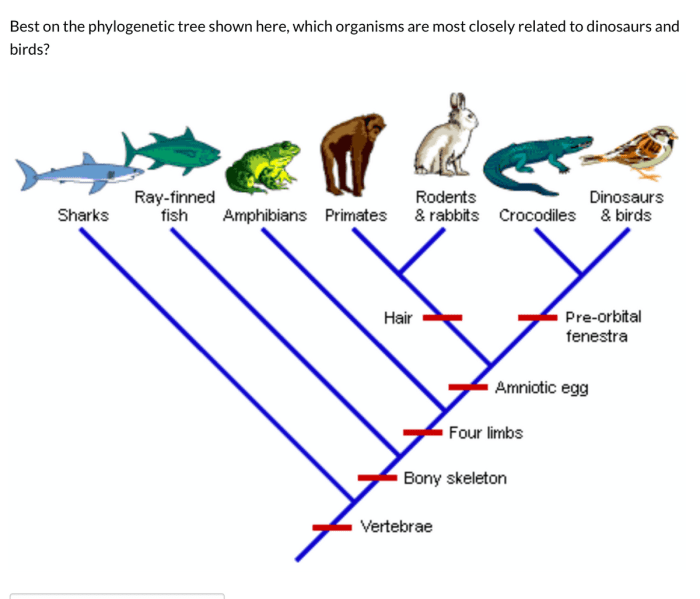
A phylogenetic tree, also known as an evolutionary tree, is a diagram that represents the evolutionary relationships among different species or other taxa. It is a branching diagram that shows the hypothesized evolutionary history of a group of organisms, based on shared characteristics and genetic similarities.
A simple phylogenetic tree might look like this:
“` +——-+ | | | A | +——-+ | V +——-+ | | | B | +——-+ | V +——-+ | | | C | +——-+ “`
In this tree, species A is the most closely related to species B, and both are more closely related to species C than to any other species. The branches of the tree represent the evolutionary relationships between the species, with the length of the branches indicating the amount of evolutionary change that has occurred.
Different Types of Phylogenetic Trees, Phylogenetic tree practice worksheet with answers
There are many different types of phylogenetic trees, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Some of the most common types of phylogenetic trees include:
- Cladograms:Cladograms are the most basic type of phylogenetic tree. They show the branching relationships between species, but they do not indicate the amount of evolutionary change that has occurred.
- Phylograms:Phylograms are similar to cladograms, but they include information about the amount of evolutionary change that has occurred. The branches of a phylogram are proportional to the amount of evolutionary change that has occurred.
- Dendrograms:Dendrograms are similar to cladograms, but they do not show the evolutionary relationships between species. Instead, they show the similarity between species, with the most similar species being placed closer together on the tree.
Q&A: Phylogenetic Tree Practice Worksheet With Answers
What is the purpose of a phylogenetic tree?
A phylogenetic tree is a diagrammatic representation of the evolutionary relationships among different species or other taxa, providing insights into their shared ancestry and patterns of divergence over time.
How are phylogenetic trees constructed?
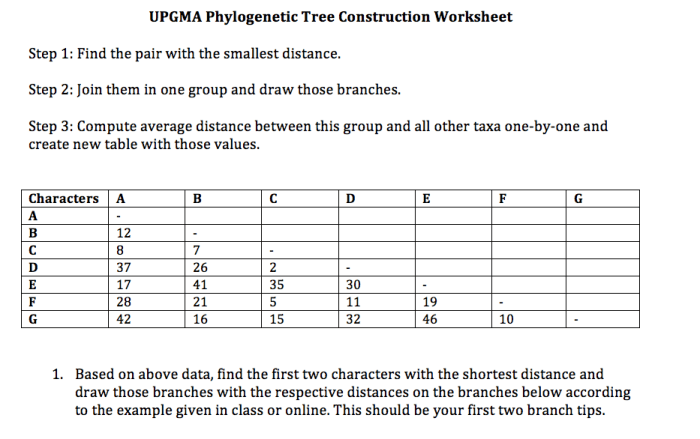
Phylogenetic trees are typically constructed using comparative data, such as DNA sequences, morphological characteristics, or fossil records. These data are analyzed using various methods, such as maximum parsimony, neighbor-joining, or Bayesian inference, to infer the most likely evolutionary relationships.
What types of information can be obtained from a phylogenetic tree?
Phylogenetic trees can provide information about the evolutionary history of species, including their common ancestors, patterns of diversification, and rates of evolution. They can also be used to infer the timing of evolutionary events, such as speciation or extinction.